Go Gin 入门教程
思维导图
Gin 简介
Gin is a HTTP web framework written in Go (Golang). It features a Martini-like API with much better performance – up to 40 times faster. If you need smashing performance, get yourself some Gin.
Gin 是使用 Go/golang 语言实现的 HTTP Web 框架。接口简洁,性能极高。截止 1.4.0 版本,包含测试代码,仅14K,其中测试代码 9K 左右,也就是说框架源码仅 5K 左右。
$ find . -name "*_test.go" | xargs cat | wc -l
8657
$ find . -name "*.go" | xargs cat | wc -l
14115
Gin 特性
- 快速:路由不使用反射,基于Radix树,内存占用少。
- 中间件:HTTP请求,可先经过一系列中间件处理,例如:Logger,Authorization,GZIP等。这个特性和 NodeJs 的
Koa框架很像。中间件机制也极大地提高了框架的可扩展性。 - 异常处理:服务始终可用,不会宕机。Gin 可以捕获 panic,并恢复。而且有极为便利的机制处理HTTP请求过程中发生的错误。
- JSON:Gin可以解析并验证请求的JSON。这个特性对
Restful API的开发尤其有用。 - 路由分组:例如将需要授权和不需要授权的API分组,不同版本的API分组。而且分组可嵌套,且性能不受影响。
- 渲染内置:原生支持JSON,XML和HTML的渲染。
安装Go & Gin
初学者建议先阅读 Go 语言简明教程。
一篇文章介绍了 Go 基本类型,结构体,单元测试,并发编程,依赖管理等内容。Go 1.13 以上版本的安装推荐该教程的方式。
- 安装 Go (Ubuntu)
$ sudo apt-get install golang-go
$ go version
# go version go1.6.2 linux/amd64Ubuntu自带版本太老了,安装新版可以使用如下命令。
$ sudo add-apt-repository ppa:gophers/archive
$ sudo apt-get update
$ sudo apt-get install golang-1.11-go
默认安装在/usr/lib/go-1.11,需要将/usr/lib/go-1.11/bin手动加入环境变量。在 .bashrc 中添加下面的配置,并 source ~/.bashrc
export PATH=$PATH:/usr/lib/go-1.11/bin
- 安装 Go (Mac)
$ brew install go
$ go version
# go version go1.12.5 darwin/amd64- 设置环境变量
在 ~/.bashrc 中添加 GOPATH 变量
export GOPATH=~/go
export PATH=$PATH:$GOPATH/bin
添加完后,source ~/.bashrc
- 安装一些辅助的工具库
由于网络原因,不能够直接访问 http://golang.org,但相关的库已经镜像到 Golang – Github
例如,直接安装 go-outline 时会报网络错误,因为golang.org/x/tools是go-outline的依赖库。
$ go get -u -v github.com/ramya-rao-a/go-outline
github.com/ramya-rao-a/go-outline (download)
Fetching https://golang.org/x/tools/go/buildutil?go-get=1
https fetch failed: Get https://golang.org/x/tools/go/buildutil?go-get=1:
dial tcp 216.239.37.1:443: i/o timeout
因此,可以先从 Github 手动安装好,再安装 go-outline 和 goreturns。
git clone https://github.com/golang/tools.git $GOPATH/src/golang.org/x/tools
go get -v github.com/ramya-rao-a/go-outline
go get -v github.com/sqs/goreturns
go get -v github.com/rogpeppe/godef
Go语言有大量的辅助工具,如果你使用VSCode,将会提示你将必要的工具,例如静态检查、自动补全等工具依次安装完毕。
- 安装 Gin
go get -u -v github.com/gin-gonic/gin
-v:打印出被构建的代码包的名字-u:已存在相关的代码包,强行更新代码包及其依赖包
第一个Gin程序
在一个空文件夹里新建文件main.go。
// geektutu.com
// main.go
package main
import "github.com/gin-gonic/gin"
func main() {
r := gin.Default()
r.GET("/", func(c *gin.Context) {
c.String(200, "Hello, Geektutu")
})
r.Run() // listen and serve on 0.0.0.0:8080
}
- 首先,我们使用了
gin.Default()生成了一个实例,这个实例即 WSGI 应用程序。 - 接下来,我们使用
r.Get("/", ...)声明了一个路由,告诉 Gin 什么样的URL 能触发传入的函数,这个函数返回我们想要显示在用户浏览器中的信息。 - 最后用
r.Run()函数来让应用运行在本地服务器上,默认监听端口是 _8080_,可以传入参数设置端口,例如r.Run(":9999")即运行在 _9999_端口。
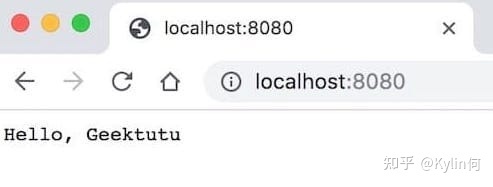
- 运行
$ go run main.go
[GIN-debug] GET / --> main.main.func1 (3 handlers)
[GIN-debug] Environment variable PORT is undefined. Using port :8080 by default
[GIN-debug] Listening and serving HTTP on :8080
- 浏览器访问
http://localhost:8080
路由(Route)
路由方法有 GET, POST, PUT, PATCH, DELETE 和 OPTIONS,还有Any,可匹配以上任意类型的请求。
无参数
// 无参数
r.GET("/", func(c *gin.Context) {
c.String(http.StatusOK, "Who are you?")
})
$ curl http://localhost:9999/
Who are you?curl参数可参考https://man.linuxde.net/curl
解析路径参数
有时候我们需要动态的路由,如 /user/:name,通过调用不同的 url 来传入不同的 name。/user/:name/*role,* 代表可选。
// 匹配 /user/geektutu
r.GET("/user/:name", func(c *gin.Context) {
name := c.Param("name")
c.String(http.StatusOK, "Hello %s", name)
})
$ curl http://localhost:9999/user/geektutu
Hello geektutu获取Query参数
// 匹配users?name=xxx&role=xxx,role可选
r.GET("/users", func(c *gin.Context) {
name := c.Query("name")
role := c.DefaultQuery("role", "teacher")
c.String(http.StatusOK, "%s is a %s", name, role)
})
$ curl "http://localhost:9999/users?name=Tom&role=student"
Tom is a student
获取POST参数
// POST
r.POST("/form", func(c *gin.Context) {
username := c.PostForm("username")
password := c.DefaultPostForm("password", "000000") // 可设置默认值
c.JSON(http.StatusOK, gin.H{
"username": username,
"password": password,
})
})
$ curl http://localhost:9999/form -X POST -d 'username=geektutu&password=1234'
{"password":"1234","username":"geektutu"}
Query和POST混合参数
// GET 和 POST 混合
r.POST("/posts", func(c *gin.Context) {
id := c.Query("id")
page := c.DefaultQuery("page", "0")
username := c.PostForm("username")
password := c.DefaultPostForm("username", "000000") // 可设置默认值
c.JSON(http.StatusOK, gin.H{
"id": id,
"page": page,
"username": username,
"password": password,
})
})
$ curl "http://localhost:9999/posts?id=9876&page=7" -X POST -d 'username=geektutu&password=1234'
{"id":"9876","page":"7","password":"1234","username":"geektutu"}
Map参数(字典参数)
r.POST("/post", func(c *gin.Context) {
ids := c.QueryMap("ids")
names := c.PostFormMap("names")
c.JSON(http.StatusOK, gin.H{
"ids": ids,
"names": names,
})
})
$ curl -g "http://localhost:9999/post?ids[Jack]=001&ids[Tom]=002" -X POST -d 'names[a]=Sam&names[b]=David'
{"ids":{"Jack":"001","Tom":"002"},"names":{"a":"Sam","b":"David"}}
重定向(Redirect)
r.GET("/redirect", func(c *gin.Context) {
c.Redirect(http.StatusMovedPermanently, "/index")
})
r.GET("/goindex", func(c *gin.Context) {
c.Request.URL.Path = "/"
r.HandleContext(c)
})
$ curl -i http://localhost:9999/redirect
HTTP/1.1 301 Moved Permanently
Content-Type: text/html; charset=utf-8
Location: /
Date: Thu, 08 Aug 2019 17:22:14 GMT
Content-Length: 36
<a href="/">Moved Permanently</a>.
$ curl "http://localhost:9999/goindex"
Who are you?
分组路由(Grouping Routes)
如果有一组路由,前缀都是/api/v1开头,是否每个路由都需要加上/api/v1这个前缀呢?答案是不需要,分组路由可以解决这个问题。利用分组路由还可以更好地实现权限控制,例如将需要登录鉴权的路由放到同一分组中去,简化权限控制。
// group routes 分组路由
defaultHandler := func(c *gin.Context) {
c.JSON(http.StatusOK, gin.H{
"path": c.FullPath(),
})
}
// group: v1
v1 := r.Group("/v1")
{
v1.GET("/posts", defaultHandler)
v1.GET("/series", defaultHandler)
}
// group: v2
v2 := r.Group("/v2")
{
v2.GET("/posts", defaultHandler)
v2.GET("/series", defaultHandler)
}
$ curl http://localhost:9999/v1/posts
{"path":"/v1/posts"}
$ curl http://localhost:9999/v2/posts
{"path":"/v2/posts"}
上传文件
单个文件
r.POST("/upload1", func(c *gin.Context) {
file, _ := c.FormFile("file")
// c.SaveUploadedFile(file, dst)
c.String(http.StatusOK, "%s uploaded!", file.Filename)
})
多个文件
r.POST("/upload2", func(c *gin.Context) {
// Multipart form
form, _ := c.MultipartForm()
files := form.File["upload[]"]
for _, file := range files {
log.Println(file.Filename)
// c.SaveUploadedFile(file, dst)
}
c.String(http.StatusOK, "%d files uploaded!", len(files))
})
HTML模板(Template)
type student struct {
Name string
Age int8
}
r.LoadHTMLGlob("templates/*")
stu1 := &student{Name: "Geektutu", Age: 20}
stu2 := &student{Name: "Jack", Age: 22}
r.GET("/arr", func(c *gin.Context) {
c.HTML(http.StatusOK, "arr.tmpl", gin.H{
"title": "Gin",
"stuArr": [2]*student{stu1, stu2},
})
})
<!-- templates/arr.tmpl -->
<html>
<body>
<p>hello, {{.title}}</p>
{{range $index, $ele := .stuArr }}
<p>{{ $index }}: {{ $ele.Name }} is {{ $ele.Age }} years old</p>
{{ end }}
</body>
</html>
$ curl http://localhost:9999/arr
<html>
<body>
<p>hello, Gin</p>
<p>0: Geektutu is 20 years old</p>
<p>1: Jack is 22 years old</p>
</body>
</html>
- Gin默认使用模板Go语言标准库的模板
text/template和html/template,语法与标准库一致,支持各种复杂场景的渲染。 - 参考官方文档text/template,html/template
中间件(Middleware)
// 作用于全局
r.Use(gin.Logger())
r.Use(gin.Recovery())
// 作用于单个路由
r.GET("/benchmark", MyBenchLogger(), benchEndpoint)
// 作用于某个组
authorized := r.Group("/")
authorized.Use(AuthRequired())
{
authorized.POST("/login", loginEndpoint)
authorized.POST("/submit", submitEndpoint)
}
如何自定义中间件呢?
func Logger() gin.HandlerFunc {
return func(c *gin.Context) {
t := time.Now()
// 给Context实例设置一个值
c.Set("geektutu", "1111")
// 请求前
c.Next()
// 请求后
latency := time.Since(t)
log.Print(latency)
}
}
热加载调试 Hot Reload
Python 的 Flask框架,有 debug 模式,启动时传入 debug=True 就可以热加载(Hot Reload, Live Reload)了。即更改源码,保存后,自动触发更新,浏览器上刷新即可。免去了杀进程、重新启动之苦。
Gin 原生不支持,但有很多额外的库可以支持。例如
这次,我们采用 http://github.com/pilu/fresh 。
go get -v -u github.com/pilu/fresh
安装好后,只需要将go run main.go命令换成fresh即可。每次更改源文件,代码将自动重新编译(Auto Compile)。





联系站长
友情链接
其他入口
QQ与微信加好友
粤ICP备17018681号 站点地图 www.iamdu.com 版权所有 服务商提供:阿里云 Designed by :DU
本站部分资源内容来源于网络,若侵犯您的权益,请联系删除!